Building up the Open Knowledge Base
So many teachers worry about role of Artificial Inteligence. Will kids hand in every paper written by ChatGPT? Does the use of AI reduce cognitive load so much that learning decay increases as retention decreases? Can kids learn without the struggle?
Yet if you teach learners to openly contribute to the knowledge base their work may show up in the corpus, or the sources, of Artificial Intelligence.
Basically, if you edit Wikipedia you are the AI.
Wikipedia in Research
Before teachers fretted about Artificial Intelligence and Large Language Models we worried about Wikipedia. To this day you will hear many educators call Wikipedia unreliable and warn students not to use it in research. That advice falls short as misguided based on bad assumptions.
First you need to know Wikipedia, like any Encyclopedia is not a primary source. They rely on sourcing other evidence to support their claims. Wikipedia specifically relies on secondary sources. Meaning an editor does not do original research looking for artifacts to summarize. Instead an editor wants to find evidence published in secondary sources such as the Press or research articles. The more times a claim gets supported by evidence in secondary sources the more reliability gets weighted.
Critics often note that, “Anyone can edit Wikipedia.”
Feature, not bug. Also, technically not true. Some articles have protections that only only allow extended confirmed editors to make changes. This means you have had to had made 500 edits before and can not have a brand new account. This helps to fight vandalism and efforts to control the narrative.
Nation states and Public Relations firms do fight over Wikipedia. The articles make up the backbone of search results and the large language models we erroneously call Artificial Intelligence. To counter this reality tens of thousands of editors help to craft the Encyclopedia
I have edited Wikipedia since 2009. Fourteen years. If you ask AI to define “Situated Cognition” often the first sentence I ever wrote on Wikipedia shows up in your definition.
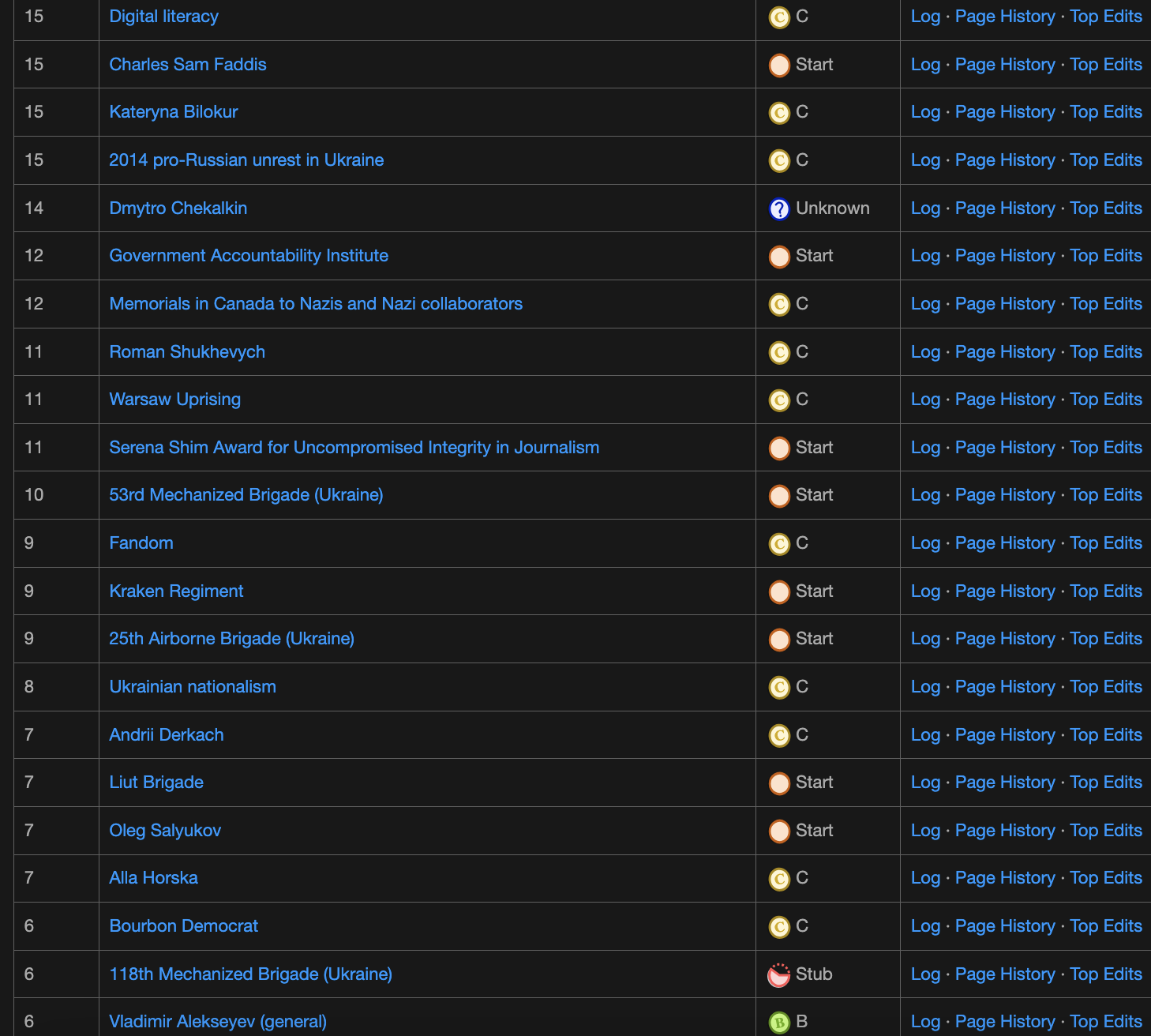
Lately I focus on articles around Ukrainian history and russia’s illegal invasion and ethnic cleansing in Ukraine. I still edit articles in the field of cognitive science as well (these need lots of work)
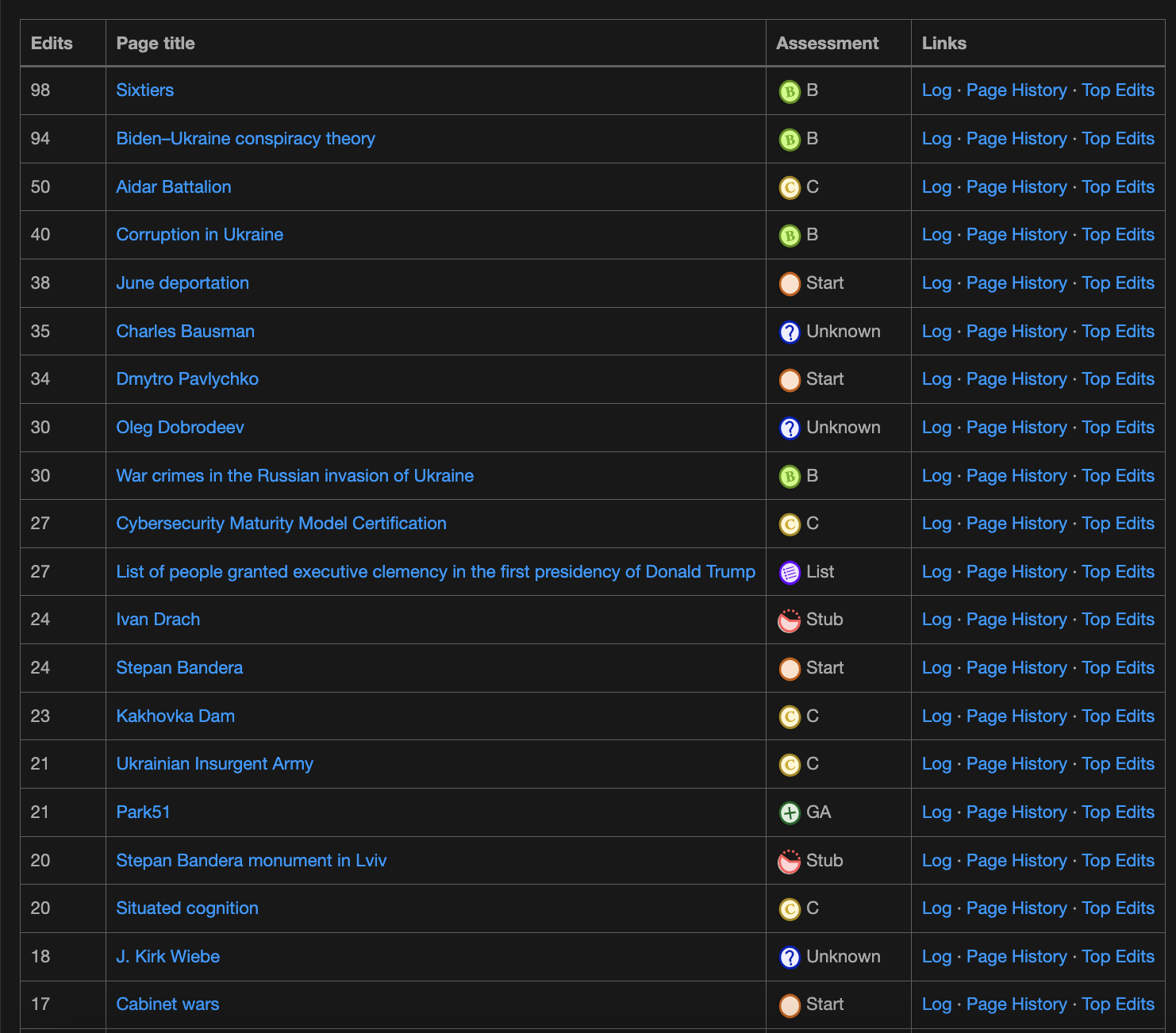
In these screenshots you see articles where I have made a majority of my edits. You also see a quality ranking. When you have students learn about Wikipedia teach them to examine the quality rating of an article. Have them examine the talk page to see if the article has sparked debate. Examine the edit history to make judgements about currency
Wikis in the Classroom
You can use Wikipedia in the classroom. We have large volunteer groups focused on developing lessons and ideas to get student to edit Wikipedia.
Yet you can also use any wiki in the classroom to build in the social practices of contributing to Knowledge Commons. You can choose many of the free wikis for educators. You can also utilize Google Docs as a public document and have it act very similar to a wiki. Same with Google Sites.
Set Class expectations
What do you want students to know and do after your wiki assignment. Cover the consequences of vandalism or publishing inapprotpriate content. Let them see the audit logs
Start Small
So many educators, often college professors, will assign a wikipedia article to edit before students have expereience. Every wiki has a culture. You need to begin by building one in your classroom. You want students making many small edits over time. Too often people want to edit an entire article in Google Docs and then cut and paste it into a wiki. Teach students to make small edits, and to publish a revision after each claim and evidence gets added.
Create Schoolwide Wikis
You do not have to have a wiki just for each class. In fact you can build school culture by creating a school wide wiki. Students across multiple grades and years can contribute
Edit Logs Drive Assessment
Wikis provide an audit log of when edits get made by a particular student. This creates wonderful assessment data.
Collaborate
You want students to work together. You can adapt Literature Circles and Reciprocal Teaching to wikis. Either assign teams to articles or create roles. Students can serve as lead editors, researchers, fact checkers, or style editors.
Text Structure
Wikis work best with a common text structure, In fact teaching students to write wiki articles provides wonderful opportunities for text structure lessons. Come up with an article template for students
Classroom Ideas
Almost any written assignment can work for a wiki. Fiction or non-fiction.
1. Art and Culture
Beginning with art and culture, rather than a controversial topic helps. Especially if editing wikipedia. You build the culture. Now art can and should cause controversy but you can focus on historical details.
2. Historical Timelines
Timelines and biographies make for great wiki topics.
3. Short Stories
The first collaborative article my students wrote, on Google Docs, before Google even bought it and made it Google Docs, was a short story about a mean Cafeteria lady. Wikis do not have to be non-fiction.
These are just three ideas for wikis in the classroom. Really you can take them in so many ways.
Img credit: The tree of knowledge flickr photo by .^.Blanksy shared under a Creative Commons (BY-NC-SA 2.0) license
**
